|
OpenPDM makes 3D data available worldwide at BroseBy Udo Hering Engineers at numerous companies still prepare their 3D data manually in order to make it digitally available to colleagues in purchasing or production planning. Not so at the Brose Group. The manufacturer of mechatronic components and systems for the automotive industry has completely automated the preparation, conversion and provision of CATIA data in JT format using PROSTEP solutions. 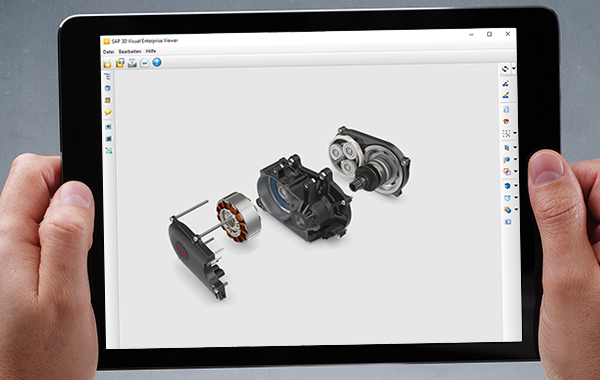
With 26,000 employees and annual revenues of 6.2 billion euros, the Bamberg-headquartered Brose Group ranks among the world’s top 40 automotive suppliers. Every second new vehicle that rolls off the production line worldwide is equipped with at least one Brose product to increase safety, comfort and efficiency. The core competence of the company, whose success story began with a crank drive for retracting car windows, is the synthesis of mechanical, electrical, electronic and sensor systems. The product range includes door systems, liftgates, adjustment systems for front and rear seats as well as electric motors and drives for a number of different of uses in vehicles. The (autonomous) driving experience of the future begins as soon as you get in a vehicle – with doors that open automatically, provided that there is nothing in way, seats that adjust automatically to whoever is driving and a preheated vehicle interior. Door, closure and seating systems are thus becoming complex, mechatronic or even cyberphysical systems whose development not only requires new tools, methods and processes but also a more efficient use of existing information. "Far too much information is still contained in TIFF and PDF/A documents and is therefore not available in digital form to downstream processes," says Walter Redinger, head of Development and Production Systems/Information Systems at Brose. The IT department has therefore defined a clear digitalization strategy together with the company's business operations. In addition to the automation of design processes using assistance systems and the virtual validation of prototypes, it also involves an approach to OEM collaboration that is oriented to a greater extent towards, for example, systems/model-based systems engineering (MBSE) and the use of new technologies such as augmented reality (AR). The objective is to have a digital master that not only includes the 3D models but also the electrics/electronics (E/E) information and software versions and makes all this information digitally available. Multi-layer PLM landscape Redinger goes on to say that the key to digitalization is an end-to-end PLM tool chain that covers everything from requirements management to designing the software, printed circuit boards and mechanical components through to test procedures and simulation, including digital production planning and control. "The aim behind this end-to-end digitalization is to integrate the individual disciplines more tightly and enhance the core efficiencies in the processes. This not only requires cultural change in the organization but also places new demands on our PLM landscape." The PLM landscape at Brose comprises multiple layers. The PLM backbone is a SAP system that is used to create parts, materials and BOMs, approve drawings and manage changes. It is closely integrated with MS SharePoint, which 5,000 Brose employees worldwide use to handle their customer projects. ENOVIA VPM, the team data management (TDM) system used for mechanical and E/E development to date, is currently being replaced by the 3DEXPERIENCE (3DX) platform. The software developers are currently still using Virtual DOORS software and the Rational Suite set of tools for application lifecycle management (ALM) but will gradually be switching to codeBeamer ALM software solution. As Redinger says, OpenPDM assumes the role of a hub for connecting the different environments within the PLM landscape. This applies in particular to the successfully implemented project for ENOVIA/3DX-SAP integration, which allows CATIA data to be converted into JT format and made available worldwide. Brose has used the integration platform and PROSTEP's services in the past, for example to provide joint venture partners with selected data and synchronize it at regular intervals. The solution was also used when the company took over Continental's electric motor division and the division's PLM data had to be extracted from Continental's environment. "PROSTEP is a long-standing and reliable partner with well-functioning tools and very experienced staff," says Redinger. 3D data for downstream processes Unlike other automotive suppliers, Brose uses its own CATIA environment for mechanical development rather than the system used by the respective customer. All the engineers at the 25 development sites – i.e. approximately 1,000 employees – use a uniform methodology and apply the same standards, thus making it easier to collaborate on cross-site development projects. "Working in the customer’s environment would be easier for the departments, but would make it more difficult to exploit the synergies offered by standardization and data reuse," says Redinger. The IT department nevertheless maintains about 30 different customer environments in order to prepare the CAD data and convert it into the respective customer formats. PROSTEP’s OpenDXM GlobalX data exchange platform has been managing data conversion and exchange for a number of years. Up until now, only 2D drawings derived from CATIA were transferred to the SAP document management system as TIFF or PDF/A and approved there so that they could be made available for downstream processes such as procurement or production planning. Only then did the engineers approve the associated 3D models in ENOVIA. When buyers or suppliers needed 3D models in addition to the 2D drawings to process requests for quotation, engineers had to prepare them, filter out certain details if necessary and convert them to the supplier's preferred format. The manual processing was not only time-consuming but also had the disadvantage that the purchasing department could never be sure that all suppliers had received the same level of information. In order to simplify the enterprise-wide use of 3D data, Brose implemented a solution with PROSTEP’s support that automatically triggers JT conversion when 3D data is approved in ENOVIA, or in the future in 3DX, and transfer the JT models to SAP. The solution is essentially based on OpenPDM with connectors to ENOVIA/3DX and SAP as well as PROSTEP’s newly developed batch processing framework (BPF), which manages the third-party converter for converting CATIA data into JT and other formats already available at Brose. When it comes to automatically importing data into the PLM backbone, the data exchange platform accesses SAP web services that ensure that the JT models are correctly linked with the BOMs and can be automatically updated and versioned if changes are made. If a part or assembly is modified, a JT file with a new index is created once the part or assembly has been approved so that its development history is retained in SAP. PROSTEP has adapted the solution so that the individual process steps, from exporting the data to converting it and importing it into SAP, can be performed in parallel and independently of each other. The reason for this is that Brose also wants to gradually make 3D data from projects launched before the solution went live available in SAP. This will significantly increase the volume of data to be converted. As Redinger says, between 100 and 150 JT files are currently being uploaded to SAP every day. 
Savings in downstream processes Redinger admits that the fact that Brose needs individual parts as well as subassemblies and assemblies converted leads to certain redundancies. "But it has the advantage that the JT models can be exchanged more easily and used for downstream processes. The buyer can send them directly to the supplier, at least when requesting quotations. JT is ideal, especially in the early offer phase, because it is a uniform format with a reduced data volume that does not disclose too much know-how. It is also enjoying growing acceptance in the automotive industry." The information contained in the 3D models made available in JT format can be used in a number of different downstream processes since relatively few details are filtered out during conversion. Although product manufacturing information (PMI) is not yet embedded, the JT models are extremely helpful to production planners when they want to obtain a quick overview of the shape of certain components without having to always bother the engineers. If, however, the 3D models are to be made available earlier in the process, generating them in JT format would have to performed separate from approving drawings, says Redinger – possibly with a restriction note or for a selected group of users. In general, all employees with access to the PLM backbone also have access to the JT models. A simple JT viewer is available in SAP for displaying the models. The IT department provides fee-based visualization tools with an extended functional scope to users who want to use the JT data to carry out clash detection analysis for example. However, this only applies to internal users. In the case of suppliers, Brose recommends that they use the free JT2Go viewer. The company's objective is to get all its suppliers to start using JT over the course of the next few months so that it can do away with manual conversion entirely. It is not only the engineers who benefit from automatic JT conversion. "We are seeing significant savings in the downstream processes – thanks in part to the format’s clear-cut structure," says Redinger. He expects additional benefits from more widespread use of JT data in other application scenarios such as review processes, which are currently performed on the basis of CATIA data. The availability of 3D data in SAP lays the groundwork for the digital master, which now of course needs to be rounded off with other information that fills any gaps.

|
|
| © PROSTEP AG | ALL RIGHTS RESERVED | IMPRESSUM | DATENSCHUTZERKLÄRUNG | HIER KÖNNEN SIE DEN NEWSLETTER ABBESTELLEN. |